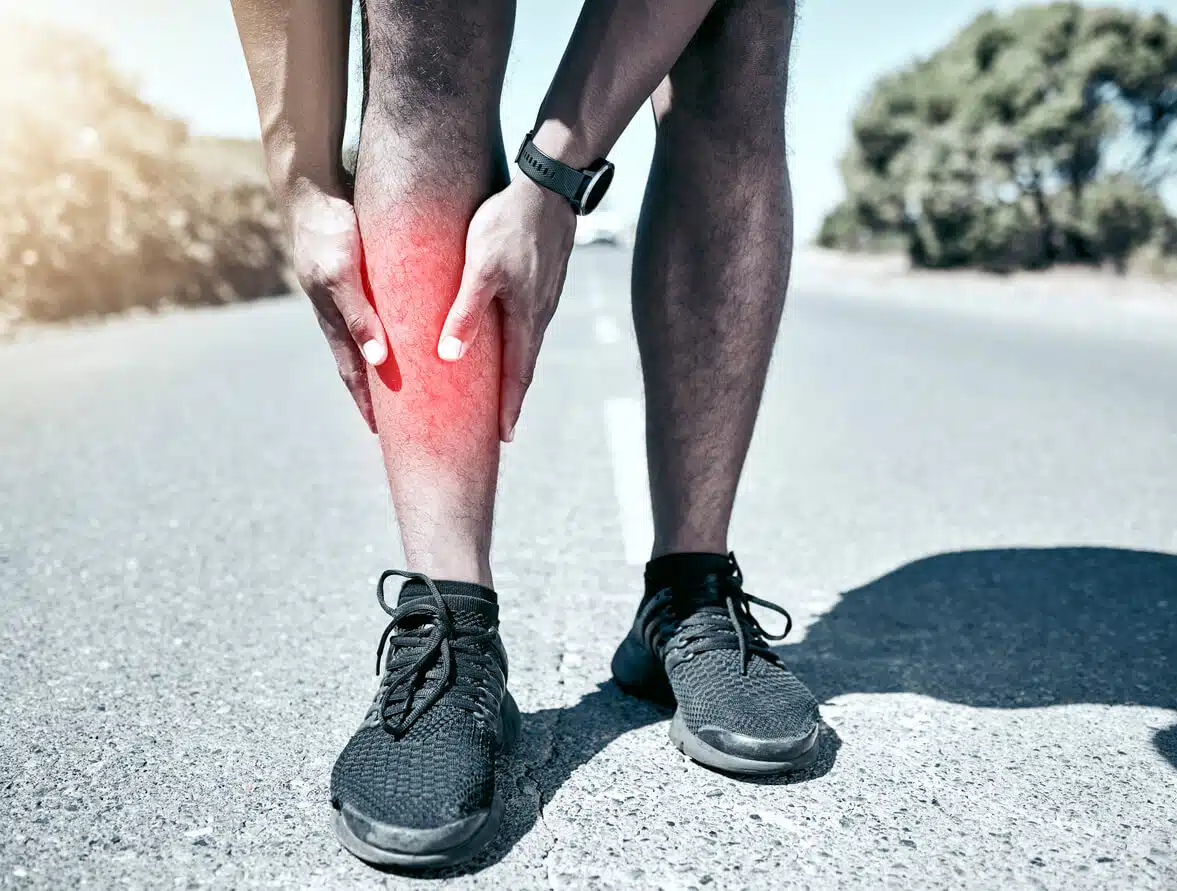
Stress fractures are small cracks or breaks in bones that are caused by repetitive stress or overuse. They commonly occur in weight-bearing bones like the feet, ankles, shins, and hips.
These injuries are often seen in athletes and people who engage in high-impact activities.
In this article, we are going to talk more about stress fractures, such as their causes and symptoms, and how they are treated.
What Causes Stress Fractures?
Athletes are at risk of stress fractures due to the nature of their activities and the demands of their lifestyle. Individuals with health conditions that affect the mineral density of the bones are also susceptible to stress fractures.
The most common cause of stress fractures include:
● Overtraining
A sudden increase in the intensity or frequency of sports or exercise quickly can overload the bones, leading to stress fractures.
● Improper footwear
Wearing shoes that don’t provide proper support or cushioning can increase the risk of stress fractures. Make sure you are wearing the appropriate footwear for your chosen activity.
● Poor biomechanics
Abnormal foot structure or mechanics can place excessive stress on certain bones, making them more prone to fractures.
● Nutritional deficiencies
Inadequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, as well as other nutrients necessary for bone health can weaken bones and make them susceptible to fractures.
Symptoms of a Stress Fracture
In most cases, stress fractures cause noticeable symptoms. Below are just some of the symptoms of stress fractures:
- Pain that starts during physical activity and worsens
- Persistent pain even after stopping activity
- Increased pain during rest
- Tenderness when lightly touching the affected area
- Limb swelling
- Changes in gait
Sometimes, pain from a stress fracture can be attributed to other factors. It is important to note that even if a stress fracture is not causing noticeable symptoms, it still requires proper diagnosis and treatment to prevent further complications.
Healing After a Stress Fracture
Most stress fractures heal without the need for surgery. However, that doesn’t mean it should not be examined by a doctor who can physically examine the limb and possibly order an imaging test such as an X-ray. This is to rule out other conditions that may be causing the symptoms and to assess the stress fracture’s progression.
A patient’s stress fracture treatment may include the following:
Rest
The first step in healing a stress fracture is to rest and avoid activities that aggravate the injury, especially the sport or activity that caused the fracture. Your doctor will advise you on which specific movements to avoid. If you have a fracture on a weight-bearing joint, such as your ankle, you need to minimize putting weight on the affected leg.
Ice and Elevation
Applying ice packs and elevating the injured limb can help reduce pain and swelling. Ice should be applied during the first 72 hours of the injury.
Pain Management
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen may be recommended to relieve pain and swelling associated with stress fractures. These medications are designed for short-term use only.
Assistive Devices
A walking boot or crutches are commonly used in fracture treatment. They keep the limb immobilized and reduce excessive movement. A crutch helps to offload weight from the affected leg or foot.
Compression
Apply a compression bandage or wrap to reduce blood flow and swelling around the fracture. It can also provide minimal support to the limb. However, it is important for the compression bandage to be wrapped correctly to ensure it is not too tight, as excessive pressure can impede blood flow.
Gradual Return to Activity
Once the pain subsides and the fracture begins to heal, a physical therapist may provide guidance on gradually reintroducing weight-bearing activities. It can take anywhere from six to eight weeks to heal completely from a stress fracture.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises can help restore muscle strength, which is very important for resilience from injury and preventing stress fractures. Resistance and weight-lifting exercises that build stronger muscles also build stronger bones. Make strengthening exercise a regular part of your fitness or exercise routine.
Stress fracture surgery is usually recommended if the bone is not healing correctly. An internal fixation is a procedure that involves the use of pins and metal plates to ensure the proper positioning and eventual healing of the fracture.
Stress Fracture Treatment in North Dakota
Our orthopedic surgeons at The Bone & Joint Center in North Dakota are highly skilled in treating broken bones and injured limbs and have training at top-level trauma centers.
We offer you comprehensive care, from diagnosis to physical therapy and rehabilitation, even for patients with conditions such as osteoporosis. Our orthopedic surgeons collaborate with CHI St. Alexius trauma staff to provide comprehensive care, with multiple specialists available if necessary.
For suspected fractures, do not delay treatment. To schedule an appointment with one of our orthopedic doctors, call our office today at (701) 946-7400 / (866) 900-8650 or use our convenient online request form. Trust our highly skilled team for your trauma and fracture care and get the best results.

